Entity State Engine
The entity state engine implements concepts from a finite state machine (opens in a new tab)
ActiveQL uses the following terms
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
StateEngine | the configuration of a state machine for a StateEntity |
StateEntity | the entity that has the StateEngine configuration |
stateAttribute | the attribute of the StateEntity holding the state value |
StateEnum | the enum defining all possible state values |
TransitionEnum | the enum defining all possible transitions - this will generated |
StateEntity item | a specific item of the StateEntity |
| transition | an allowed state change from one state value to another |
| associated entities | entities having a assoc to or from the StateEntity, also over other associated entities |
| associated entity item | an item of an associated entity that references or is referenced by a specific StateEntity item |
entityStateUpdate mutation | a mutation that allows the application a transition to a StateEntity item - this will generated |
entityState query | a query allowing to see the current state value and all allowed mutations from this state for a StateEntity item - this will generated |
An entity can have one (or more) state engines that manage a state attribute. A state changes it's value either
- through a generated mutation based on allowed transitions
- after an observed mutation was successfully executed
Adding a StateEngine configuration will
- make the
stateAttributeof theStateEntityread-only - generate an
entityStateUpdatemutation - allowing to apply a transition and execute the state change - generate an
entityStatequery, allowing to see the current state value and all allowed mutations from this state - adds a validation to all observed mutations to ensure they will only be executed if any associated
StateEntityitem has a state value that is allowed - adds a afterHook to all observed mutations that can optionally change the state value of any associated
StateEntityitem after the mutation's execution.
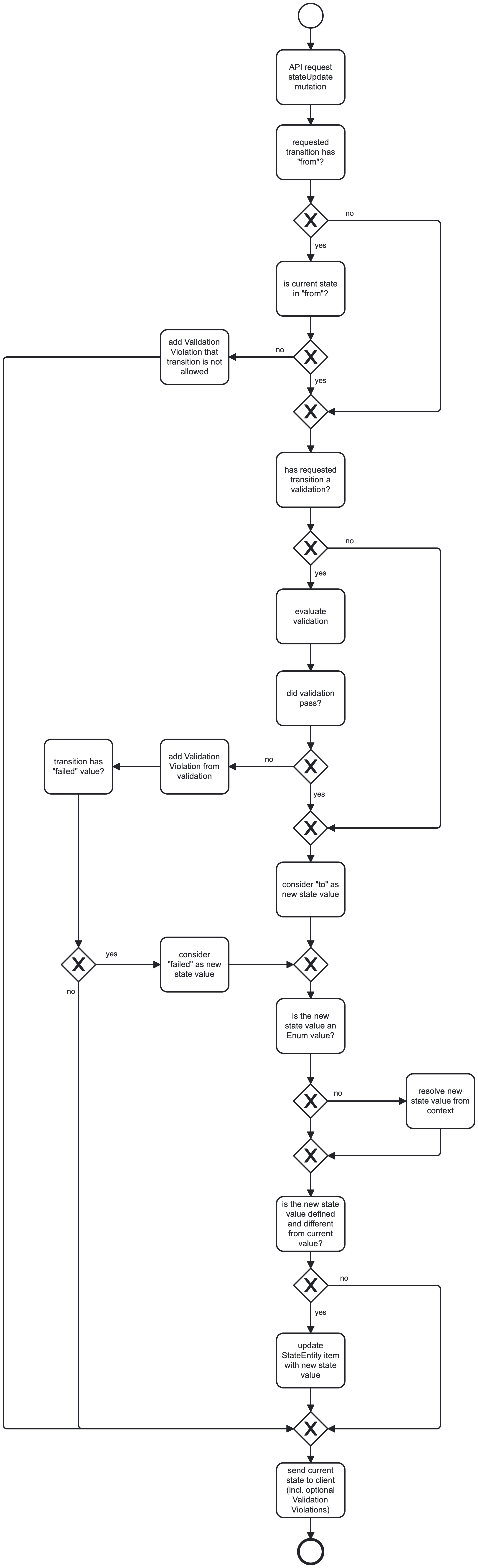
Execution of a stateUpdate mutation
Any configured transition can be applied by an API client by calling the generated entityStateUpdate mutation. This is an overview of the execution flow.
Execution of an observed mutation
Since the state of an StateEntity item can influence and is dependent of other entity items, you can observe mutations of other entities. This would be an overview of the execution flow of such a mutation.

EntityStateEngineConfig
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| stateAttribute | String | state | the entity attribute holding the state; must be of type Enum |
| initial | String | new | the default value of the stateAttribute; overrides any existing defaultValue |
| stateQueryName | String | [entity][State] | the name of the generated Query showing the current value for the stateAttribute and allowed mutations |
| stateMutationName | String | [entity][State]Update | the name of the generated Mutation allowing to apply a transition |
| transitionEnumName | String | [Entity][State]Transition | the name of the generated Enum holding all configured transition names |
| expose | boolean | true | whether the transitions should be available as an API mutation |
| observe | EntityStateEngineObserve[] | list of mutations that should be under control of this StateEngine | |
| transition | Map of StateEngineTransition | map of transitions that can be applied to change the stateAttribute value |
stateAttribute
stateAttribute: undefined | string| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
undefined | same as "state" |
string | Name of the entity attribute holding the state |
If the stateAttribute value does not match an attribute of the entity or if the attribute has another type than an Enum, the StateMachine will not be initialized.
Adding a stateAttribute will make the corresponding attribute read-only - it can only be manipulated through the generated entityStateUpdate mutation-
inital
initial: undefined | string| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
undefined | same as "new" |
string | Default value of the stateAttribute when e new StateEntity item is created |
If this does not match a value of the Enum type the stateAttribute will nonetheless be of this value, but the state engine will probably not work as expected.
transitionEnumName
transitionEnumName: undefined | string| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
undefined | same as [EntityName][StateAttributeName]Transition |
string | Name of the generated Enum holding all configured transition names |
There is usually no need for this to be configured.
expose
expose: undefined | boolean| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
undefined | same as true |
true | any transition (that does not have an expose: false) will be callable via the StateMutation |
false | no transition (except it does have an expose: true itself) will be callable via the StateMutation |
If expose: false and no transition overrides this, no StateMutation will be generated.
stateQueryName
| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
undefined | same as [entityName][StateAttributeName] |
string | Name of the generated Query showing the current value for the stateAttribute and allowed mutations |
There is usually no need for this to be configured.
entity:
Rental:
stateEngine:
stateQueryName: myRentalStatestateMutationName
| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
undefined | same as [entityName][StateAttributeName]Update |
string | Name of the generated Mutation allowing an API client to apply a transition to the StateEngine |
There is usually no need for this to be configured.
entity:
Rental:
stateEngine:
stateMutationName: myRentalStateUpdatetransition
Every transition configuration adds value to the TransitionEnum that can be applied by a client by calling the entityStateUpdate mutation.
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| from | undefined | string | string[] | state(s) in which this transition is allowed | |
| to | string | value the state should be after this transition was successfull | |
| validation | undefined | EntityStateEngineValidation | EntityStateEngineValidation[] | validation to determine whether this transition should execute the state-change to the to state-value | |
| failed | undefined | string | value the state should be after the validation of this transition failed | |
| expose | undefined | boolean | undefined | per default a transition according to the expose configuration of the StateEngine; you can override this here |
transition:
confirm:
from: requested
to: confirmOrReject # this is not an enum value, therfore resolved from the context
cancel:
from: requested
to: status
conclude:
from: confirmed
to: concluded
reopen:
from:
- rejected
- canceled
- secluded
to: requestedfrom
| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
undefined | this transition is allowed from any state |
string | same as string[] |
string[] | if the state has any of these values, the transition is allowed; if an API client attempts to apply this transition in any other state a ValidationViolation will be sent to the client and the state keeps unchanged. Any existing validation is not eveluated. |
to
| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
string | value the state should be after this transition was successfull; a transition is successfull when it is allowed and either no validation exists or the validation does not fail |
The to value is a string that is handled as follows:
- if it is a value of the
StateEnum(type of the stateAttribute) the value is used as the newstatevalue - otherwise the value is looked up the in the
context- if such a value can be found in the
contextand it is a value of theStateEnumthis value is used as the newstatevalue - if the value
- can not be found in the
contextor - the value is
undefinedor - the value is not a value of the
StateEnum- thestatekeeps unchanged
- can not be found in the
- if such a value can be found in the
validation
| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
FeelExpressionConfig | any valid FEEL Expression |
DtConfig | any valid Decision Table configuration |
DtRef | any valid reference to a Decision Table configuration in the DomainGraph |
The expressions and decision table rules have access to the context that as the following content:
| Context value | Description |
|---|---|
typeQueryName | the StateEngine item is available under the type query name of the entity, e.g. the Rental item would be available as rental |
principal | if a Principal is present in the API call it is available under principal |
locale | the current locale as determined from the runtime configuration or API call |
| associated entities | any associated entity item as defined in the context configuration |
| variables | any variable defined by the context configuration |
The return values from the expression or decision table are considered as follows:
| Return Value | Description |
|---|---|
true | undefined | null | empty string | validation did pass |
false | validation failed; a ValidationViolation with a generic message is send to the API client |
string | string[] | validation failed; the return values are send as message of a ValidationViolation to the client |
failed
| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
undefined | when a validation failes, the state keeps unchanged |
string | value the state should be after this the validation fails |
For the eveluation of the actual new state value the same rules apply as for to.
observe
Any mutation of an associated entity that can only be executed in certain states can be added to the observe list.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| mutation | string | string[] | mutation that should be oserved |
| entity | string | string[] | entity which mutations should be oserved |
| query | string | when the entity of the the observed mutation(s) has no direct assoc to the StateEntity you must provide a way to find the affected StateEntity items |
| from | string | string[] | state value(s) in which the mutations is allowed |
| to | string | new state value of the StateEntity items after the execution of the mutation |
| validation | FeelExpressionConfig | DtConfig | DtRef | ConfigSourceFn | validation if the StateEntity item would be in a valid state after the mutation was executed |
observe:
- mutation: createRental
to: requested
- mutation:
- updateRental
- deleteRental
from:
- requested
- rejected
- mutation: updateCar
from:
- requested
- rejected
- canceled
- mutation: deleteCar
from:
- requested
- confiremed
- rejected
- canceled
to: canceled
- mutation: updateDriver
from:
- requested
- rejected
- canceled
- mutation: deleteDriver
to: canceled
- entity: Destination # meaning create, update and delete mutations
from: requested
- entity: SpeedViolation
assoc: driver.rentals
from:
- requested
- canceledmutation
An observe configuration must have either a mutation or entity config value.
| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
string | same as string[] |
string[] | list of mutations that are observed by this StateEngine |
entity
When providing an entity it is treated the same as adding the
- createMutation
- updateMutation
- createMutation
| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
string | same as string[] |
string[] | list of entities that are observed by this StateEngine |
query
When you oberve mutations of an entity the StateEngine from the StateEntity hooks itself into the lifecycle methods of the observed entity. When a mutation is resolved it has to decide if there are any items of the observed entity are associated to the item that is handled by the mutation resolve.
As long as there is a direct assoc between the observed entity and the StateEntity this can be determined by this assoc. When the observed entity and the StateEntity are linked through other entity assocs you must provide the query path from the item of the observed entity to any item of the StateEntity.
The query path is the same as you would use in query.
from
| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
undefined | this transition is allowed from any state |
string | same as string[] |
string[] | if the state has any of these values, the observed mutation is allowed; if an API client attempts to apply this mutation in any other state a ValidationViolation will be added to muatation response to the client and the state keeps unchanged. Any other validation is not eveluated. |
to
| Config Value | Description |
|---|---|
undefined | the state remains unchanged after the observed mutation was executed |
string | value the state should be after the observed muation was successfully executed; meaning no validation exists or the validation does not fail |
It is evaluated like the to property of the transition.
validation
It is evaluated like the validation property of the transition. Please refer to the documentation there.
context
Any validation or evaluation of a state uses a context. This context always has the following default properties:
| Property | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
runtime | Runtime | the current runtime instance | |
principal | Principal | the principal present in the current request or undefined | |
locale | string | en | the locale present in the current request |
log | ErrorLog | the log from the current runtime | |
now | Date | new Date() | the date at creation of the context as determined by the runtime.now function |
data | any | { [typeQueryName]: Item } | |
validationViolations | ValidationViolation[] | [] |
When you provide a resolve function for a config source, this is the context you will get your callback.
When using FEEL expressions or Decision Tables the only relevant property is the data object. The data object is the evaluation context of your expressions.
assoc
Per default you find the item of the StateEntity that is evaluated whether a transition or mutation is allowed under its typeQueryName in the data object. E.g. when you have a Rental as StateEntity the data object will just have the rental item as follows:
{
rental: {
status: 'requested',
from: '2023-12-01',
till: '2023-12-03',
carId: 'xoFcO7DtgnNHEoQ2',
driverIds: [ 'xlDGd0CQY1N3EtCh', '54srKaQFFdzntImP' ],
id: 'JYD6EQBTq4PrYe3b',
indication: '[Rental:JYD6EQBTq4PrYe3b]',
createdAt: '2023-12-20T17:37:03.042Z',
updatedAt: '2023-12-20T17:37:03.048Z',
__typename: "Rental"
}
}We can use this data/object in any FEEL expressions or Decision Tables. But in most real life scenarios we would also need information from associated entities. You can add any to associated entities as you would in a GrahQL query.
With the following paths in the assoc array ...
context:
assoc:
- car
- drivers.speedViolations
- drivers.address
- destinations... we will have the all these objects in the context.data:
// {
// rental: {
// status: 'requested',
// from: '2023-12-01',
// till: '2023-12-03',
// carId: 'uPLW6HBLn8vQ6oNa',
// driverIds: [ 'zZaIjIUA5TescTOI', '0jWAeZjQ1rkSmpIW' ],
// createdAt: '2023-12-20T17:53:46.836Z',
// updatedAt: '2023-12-20T17:53:46.842Z',
// __typename: 'Rental',
// id: 'fPd5HDCdPKlLWJPz',
// indication: '[Rental:fPd5HDCdPKlLWJPz]',
// car: {
// brand: 'Smart',
// power: 94,
// createdAt: '2023-12-20T17:53:46.672Z',
// updatedAt: '2023-12-20T17:53:46.752Z',
// __typename: 'Car',
// id: 'uPLW6HBLn8vQ6oNa',
// indication: 'Smart'
// },
// drivers: [
// {
// lastname: 'Ortiz',
// birthdate: '1950-08-27',
// createdAt: '2023-12-20T20:10:31.359Z',
// updatedAt: '2023-12-20T20:10:31.458Z',
// __typename: 'Driver',
// id: 'qH87NKOdkzypjMaK',
// indication: 'Ortiz',
// speedViolations: [],
// address: undefined
// },
// {
// lastname: 'Kemmer',
// birthdate: '1951-08-15',
// createdAt: '2023-12-20T20:10:31.330Z',
// updatedAt: '2023-12-20T20:10:31.402Z',
// __typename: 'Driver',
// id: 'Cwv6aXuKb8miEMVk',
// indication: 'Kemmer',
// speedViolations: [],
// address: undefined
// }
// ],
// destinations: []
// }
// }
//variable
variable: EntityStateEngineContextVariable | EntityStateEngineContextVariable[]
type EntityStateEngineContextVariable = {[name:string]: EntityStateEngineExpression}
type EntityStateEngineExpression = FeelExpressionConfig|DtConfig|DtRef|string|boolean|numberYou might need the same evaluation in more than one location. You can add any value to the data object that becomes available for all following evaluations. If one variable is dependent on another you can put the variable definition(s) in a list. Any variable definitions will be evaluated in that order.
variable:
- driversWithoutViolations:
expression: count( rental.drivers )
youngestDriver:
expression: age( min( map( @drivers, "birthdate") ) )
- status: canceled